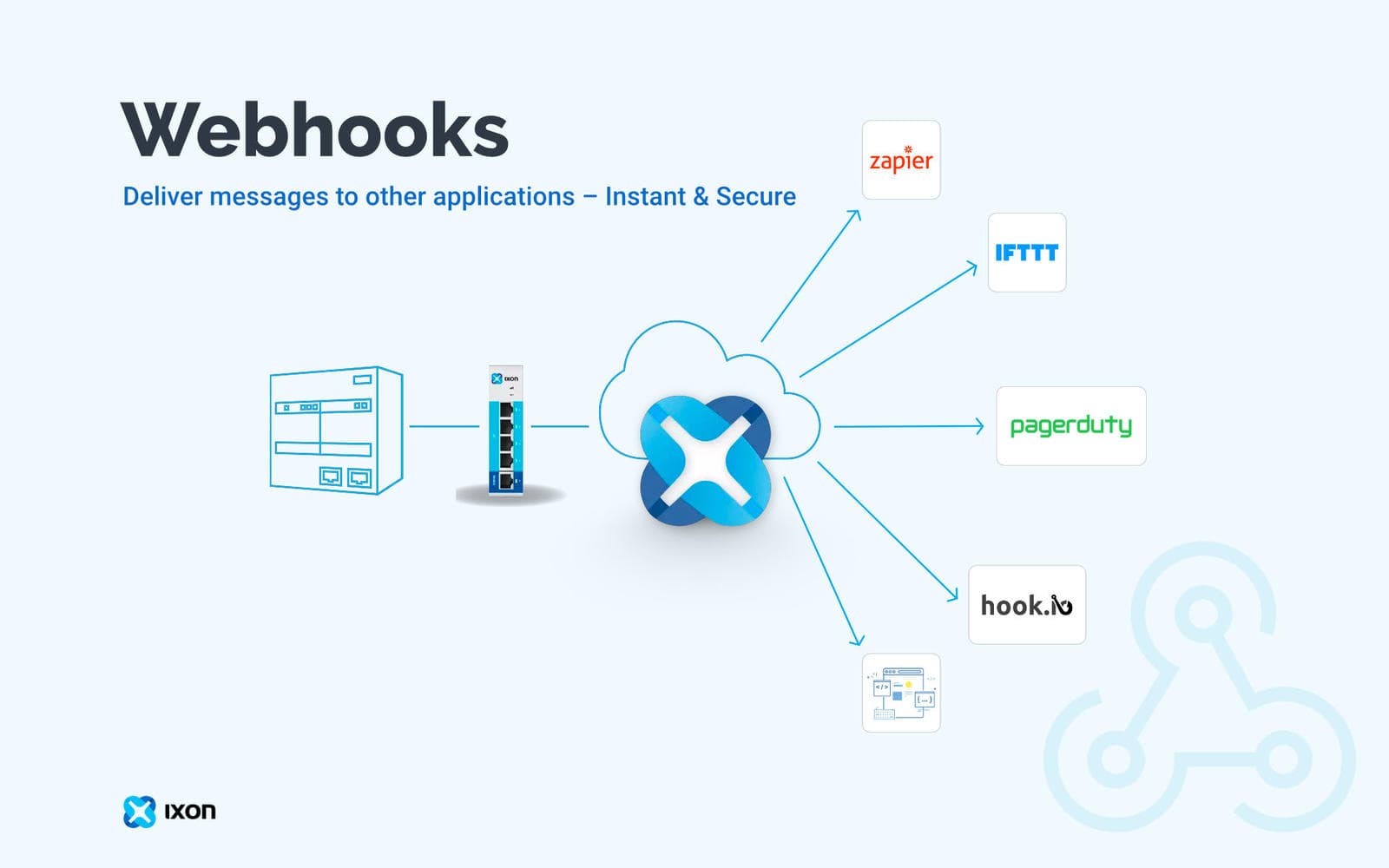
Step-by-step guide to integrating Meta's webhook system for automated Instagram comments, DMs, and WhatsApp message handling.
Understanding Meta Webhooks
Meta's webhook system allows your application to receive real-time updates about Instagram and WhatsApp activities. Instead of constantly polling their API, webhooks push updates to your server instantly.
Prerequisites
- Meta Developer Account
- Facebook App created in Meta Dashboard
- Instagram/WhatsApp Business accounts linked
- HTTPS endpoint for webhook (Meta requires SSL)
- Valid access tokens
Step 1: Setting Up Your Webhook Endpoint
Verification Endpoint
Meta first verifies your webhook endpoint:
// Using Next.js API routes
export async function GET(request) {
const searchParams = request.nextUrl.searchParams
const mode = searchParams.get('hub.mode')
const token = searchParams.get('hub.verify_token')
const challenge = searchParams.get('hub.challenge')
// Verify the webhook
if (mode === 'subscribe' && token === process.env.VERIFY_TOKEN) {
console.log('Webhook verified')
return new Response(challenge, { status: 200 })
}
return new Response('Verification failed', { status: 403 })
}Receiving Webhook Events
export async function POST(request) {
const body = await request.json()
// Verify signature
const signature = request.headers.get('x-hub-signature-256')
if (!verifySignature(body, signature)) {
return new Response('Invalid signature', { status: 401 })
}
// Process webhook
if (body.object === 'instagram') {
handleInstagramWebhook(body)
} else if (body.object === 'whatsapp_business_account') {
handleWhatsAppWebhook(body)
}
return new Response('EVENT_RECEIVED', { status: 200 })
}Step 2: Signature Verification
Always verify that requests come from Meta:
import crypto from 'crypto'
function verifySignature(body, signature) {
const expectedSignature = crypto
.createHmac('sha256', process.env.APP_SECRET)
.update(JSON.stringify(body))
.digest('hex')
return signature === `sha256=${expectedSignature}`
}Step 3: Instagram Comment Handling
Listening for Comments
async function handleInstagramWebhook(data) {
const entry = data.entry[0]
const changes = entry.changes[0]
if (changes.field === 'comments') {
const comment = changes.value
// Check if it's a new comment
if (comment.verb === 'add') {
await handleNewComment(comment)
}
}
}
async function handleNewComment(comment) {
const text = comment.text.toLowerCase()
// Keyword detection
if (text.includes('price') || text.includes('cost')) {
await replyToComment(comment.id, 'Check our website for pricing!')
} else if (text.includes('dm') || text.includes('info')) {
await replyToComment(comment.id, 'DMing you now! 💬')
await sendDirectMessage(comment.from.id, 'How can I help?')
}
}Replying to Comments
async function replyToComment(commentId, message) {
const response = await fetch(
`https://graph.facebook.com/v18.0/${commentId}/replies`,
{
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({
message: message,
access_token: process.env.INSTAGRAM_ACCESS_TOKEN
})
}
)
return response.json()
}Step 4: Instagram DM Automation
Receiving Messages
async function handleInstagramMessages(data) {
const messaging = data.entry[0].messaging[0]
if (messaging.message) {
const senderId = messaging.sender.id
const messageText = messaging.message.text
await processMessage(senderId, messageText)
}
}
async function processMessage(userId, text) {
let response = ''
// Simple bot logic
if (text.toLowerCase().includes('hello')) {
response = 'Hi! How can I assist you today?'
} else if (text.toLowerCase().includes('hours')) {
response = 'We are open Monday-Friday, 9 AM - 6 PM'
} else {
response = 'Thanks for your message! Our team will respond soon.'
}
await sendDirectMessage(userId, response)
}Sending DMs
async function sendDirectMessage(recipientId, message) {
const response = await fetch(
`https://graph.facebook.com/v18.0/me/messages`,
{
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({
recipient: { id: recipientId },
message: { text: message },
access_token: process.env.INSTAGRAM_ACCESS_TOKEN
})
}
)
return response.json()
}Step 5: WhatsApp Business Integration
Handling WhatsApp Messages
async function handleWhatsAppWebhook(data) {
const messages = data.entry[0].changes[0].value.messages
if (messages && messages[0]) {
const message = messages[0]
const from = message.from
const text = message.text.body
await handleWhatsAppMessage(from, text, message.id)
}
}Sending Template Messages
async function sendWhatsAppTemplate(phoneNumber, templateName) {
const response = await fetch(
`https://graph.facebook.com/v18.0/${PHONE_NUMBER_ID}/messages`,
{
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Authorization': `Bearer ${ACCESS_TOKEN}`,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
messaging_product: 'whatsapp',
to: phoneNumber,
type: 'template',
template: {
name: templateName,
language: { code: 'en' }
}
})
}
)
return response.json()
}Interactive Messages
async function sendWhatsAppButtons(phoneNumber, text, buttons) {
await fetch(`https://graph.facebook.com/v18.0/${PHONE_NUMBER_ID}/messages`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Authorization': `Bearer ${ACCESS_TOKEN}`,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
messaging_product: 'whatsapp',
to: phoneNumber,
type: 'interactive',
interactive: {
type: 'button',
body: { text: text },
action: {
buttons: buttons.map((btn, idx) => ({
type: 'reply',
reply: { id: `btn_${idx}`, title: btn }
}))
}
}
})
})
}Step 6: Error Handling & Retry Logic
async function makeAPICallWithRetry(url, options, maxRetries = 3) {
for (let i = 0; i < maxRetries; i++) {
try {
const response = await fetch(url, options)
if (response.ok) {
return await response.json()
}
// Handle rate limiting
if (response.status === 429) {
const retryAfter = response.headers.get('retry-after') || (i + 1) * 2
await sleep(retryAfter * 1000)
continue
}
throw new Error(`API call failed: ${response.status}`)
} catch (error) {
if (i === maxRetries - 1) throw error
await sleep((i + 1) * 1000) // Exponential backoff
}
}
}Step 7: Database Storage
Conversation History
const conversationSchema = new Schema({
userId: String,
platform: { type: String, enum: ['instagram', 'whatsapp'] },
messages: [{
from: String,
text: String,
timestamp: Date,
type: { type: String, enum: ['sent', 'received'] }
}],
status: { type: String, enum: ['active', 'resolved', 'pending'] },
lastActivity: Date
})Step 8: Production Checklist
- Security: Verify signatures on all webhooks
- Rate Limits: Implement exponential backoff
- Queue System: Use Bull or similar for async processing
- Monitoring: Log all webhook events and API calls
- Error Handling: Graceful degradation for API failures
- Scaling: Use Redis for multi-server deployments
Common Issues & Solutions
Issue: Webhook Not Receiving Events
- Verify webhook is subscribed in Meta Dashboard
- Check HTTPS certificate is valid
- Ensure endpoint responds within 20 seconds
- Verify app permissions are granted
Issue: Rate Limiting
- Implement request queuing
- Batch multiple messages when possible
- Use exponential backoff on 429 errors
- Monitor API usage in Meta Dashboard
Testing Your Integration
// Use Meta's test endpoint
const testWebhook = async () => {
await fetch('YOUR_WEBHOOK_URL', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({
object: 'instagram',
entry: [{
id: 'test',
time: Date.now(),
changes: [{
field: 'comments',
value: {
id: 'test_comment',
text: 'Test comment',
from: { id: 'test_user' }
}
}]
}]
})
})
}Results
My Meta API integration handles:
- 1000+ daily interactions across platforms
- 95% automation rate for common queries
- Sub-second response times
- 99.9% uptime with proper error handling
Conclusion
Meta's webhook system is powerful but requires careful implementation. Focus on security, error handling, and scalability from day one. Test thoroughly before going live, and monitor closely after deployment.